CHART OF SEXUAL LIFE CYCLE OF MALARIAL PARASITE
The natural ecology of malaria involves malaria...
Connect with:
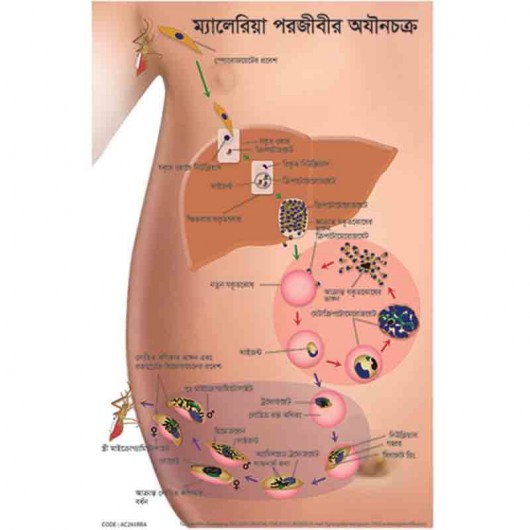
The natural ecology of malaria involves malaria parasites infecting successively two types of hosts: humans and female Anopheles mosquitoes. In humans, the parasites grow and multiply first in the liver cells and then in the red cells of the blood. In the blood, successive broods of parasites grow inside the red cells and destroy them, releasing daughter parasites (“merozoites”) that continue the cycle by invading other red cells.
Type:
The natural ecology of malaria involves malaria parasites infecting successively two types of hosts: humans and female Anophelesmosquitoes. In humans, the parasites grow and multiply first in the liver cells and then in the red cells of the blood. In the blood, successive broods of parasites grow inside the red cells and destroy them, releasing daughter parasites (“merozoites”) that continue the cycle by invading other red cells.
Type:
You are sent a comment success. The administrator will review and approve your comment. Thank you!
No customer reviews for the moment.
The natural ecology of malaria involves malaria...
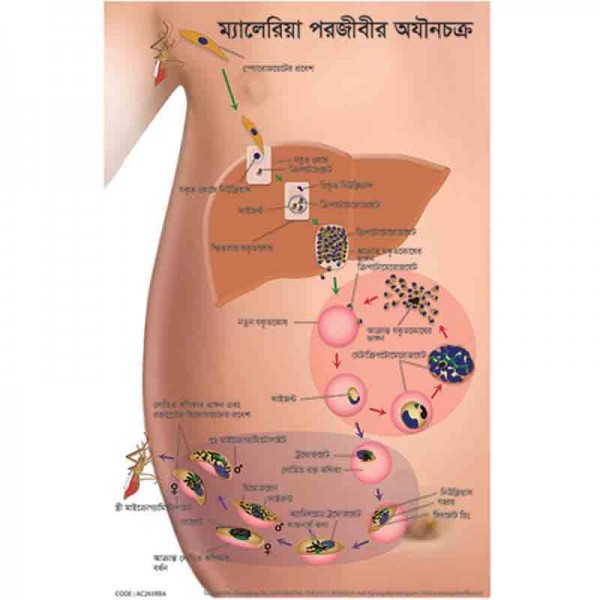
The natural ecology of malaria involves malaria parasites infecting successively two types of hosts: humans and female Anopheles mosquitoes. In humans, the parasites grow and multiply first in the liver cells and then in the red cells of the blood. In the blood, successive broods of parasites grow inside the red cells and destroy them, releasing daughter parasites (“merozoites”) that continue the cycle by invading other red cells.
Type: